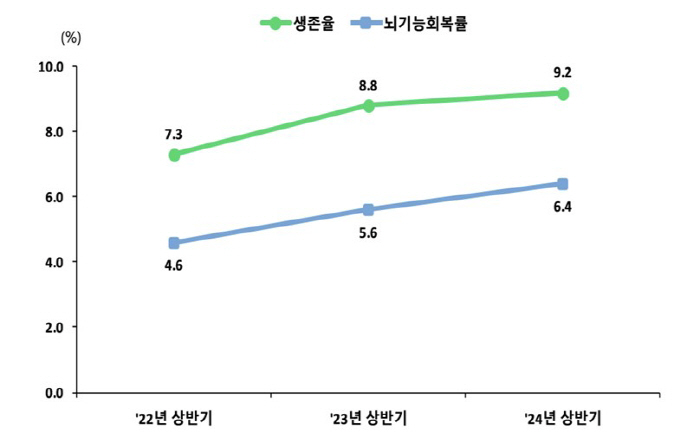
In the first half of last year, the survival rate of patients with acute cardiac arrest was 9.2%...The rate of CPR for the general public is over 30%
|
The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced the results of 16,578 (98.8%) cases of acute cardiac arrest in the first half of 2024 (January-June).
Since 2008, the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has conducted a medical record survey of acute cardiac arrest patients transferred to medical institutions by 119 paramedics through acute cardiac arrest surveys, has announced the results every half-year since 2022 so that they can be used in a timely manner for policies and research related to acute cardiac arrest.
According to the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 77.8% of acute cardiac arrest occurred in the first half of last year due to diseases such as psychogenic (myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, etc.) and stroke, and 21.8% were caused by diseases such as falls, transportation accidents, and strangulation. By location, it occurred mainly in non-public places (64.0%) such as homes and nursing institutions rather than in public places such as roads, highways, and commercial facilities (17.8%). In particular, the occurrence at home among non-public places accounted for 45.1% of the total.
The number of patients discharged alive (hereinafter 'survivor') was 1,527 cases, with a survival rate of 9.2% (up 0.4%p from 8.8% in the first half of $'23), and the number of patients discharged from the hospital with brain function restored enough to allow them to live their daily lives (hereinafter 'brain function recovery') was 6,4% (up 0.8%p from 5.6% in the first half of 23).
Amid rising interest in first aid, the survival rate and brain function recovery rate of patients have recently increased compared to the previous year, confirming that rapid response in the field, such as witnesses, is important.
According to the KDCA, the CPR implementation rate for the general public, excluding paramedics and medical personnel on duty, was 30.2% (4307 cases), up 0.4%p from 29.8% in the first half of 2023. In addition, when CPR was performed by the general public, the survival rate was 2.2 times higher and the brain function recovery rate was 3.2 times higher than when it was not performed. When CPR was performed by the general public, the survival rate was 14.3% (616 survivors) and the brain function recovery rate was 11.4% (493 brain function recovery cases). On the other hand, there were 1,393 cases where CPR was not performed by the general public, of which the survival rate was 6.4% (89 survivors) and the recovery rate of brain function was only 3.6% (50 brain function recoveries).
Ji Young-mi, Director of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said, "The upward trend in the survival rate and brain function recovery rate of patients with acute cardiac arrest is an encouraging result related to the performance of CPR by the general public. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation plays a decisive role in the survival and recovery of patients, and the role of on-site witnesses is very important, so we will continue to make various efforts such as developing educational materials and holding and promoting public CPR to further expand the role of general public." he said.
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.