Developing the world's first AI-based cholangiocarcinoma cell diagnosis technology...Accuracy 98.6%
|
Recently, a joint research team led by Professor Lee Kyung-ju and Park Se-woo of the Department of Gastroenterology at Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital of Hallym University and Professor Heo Jong-wook of the Department of Software at Hallym University developed the world's first bile duct cancer diagnosis technology that combines artificial intelligence and 3D optical diffraction tomography (hereinafter referred to as 3D ODT). This study was published in the June 2025 issue of the SCIE-level international journal 『Methods " titled 『Enhancing bile duct cancer diagnosis using AI-driven 3D photolithography』.
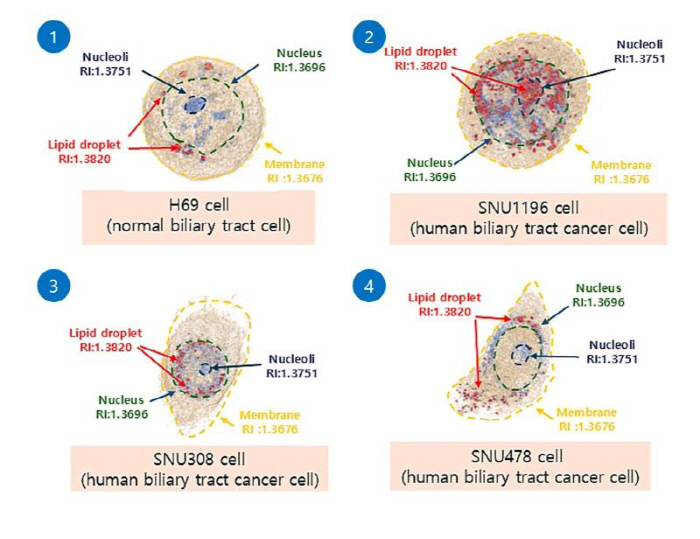
The research team paid attention to the metabolic changes in intracellular 'Lipid Droplets', one of the characteristics of cancer cells. Cancer cells have distinct metabolic differences in the volume, density, and distribution of lipid droplets compared to normal cells. The research team developed a model that automatically classifies cancer cells using 3D ODT imaging technology that can quantify this and AI-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN).
The experiments utilized bile duct cancer cell lines (SNU1196, SNU308, SNU478) and normal bile duct cells (H69), and more than 90,000 cell images were trained on CNN models. The accuracy based on single image analysis was 93.8%, and the multi-model learning accuracy including information on lipid droplets (volume, dry mass, etc.) reached 97.9%. Finally, the diagnostic accuracy of the final model applying the Multi-View Score Fusion was very high at 98.6%.
In particular, this technology is an AI-based diagnostic method that can classify cancer cells in real time only with cell images obtained without dyeing tissues separately, and is attracting attention as a new tool to assist pathological reading.
Professor Lee Kyung-ju said, `Lipid droplets are a major metabolic factor involved in energy storage, cell membrane synthesis, and stress response in cancer cells, and are also closely related to cancer invasiveness and drug resistance"This technology is highly likely to extend beyond simple image analysis to a precision diagnosis platform that reflects the metabolic characteristics of cancer cells. The newly developed diagnostic method was able to visualize lipid droplets in cells through 3D ODT, and then automatically extracted complex lipid droplets from high-dimensional images through AI to increase diagnostic accuracy", he explained.
In addition, the existing pathologic diagnosis takes several days for staining and reading after tissue collection, but this diagnostic method allows AI to identify cancer cells at the cell level in real time without staining"It is expected that it will be of practical help in quick clinical judgment and treatment decisions in the medical field."
In addition, a research team led by Professor Park Se-woo of the Department of Gastroenterology at Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, which participated in the study, developed a model that can automatically classify pancreatic cancer cells and normal cells by combining AI and 3D ODT techniques last year. The study, titled 'Automatic Recognition and Classification of Pancreatic Cancer Cells Based on Lipid Drop Analysis by 3D ODT'AI Model', was published in the April 2024 issue of the SCIE-level international journal 'Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine '.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.