Shoulder tendon damage rotator cuff tear, regardless of age
Jul 16, 2025
|
In fact, the number of rotator cuff rupture patients is steadily increasing even in their 20s and 40s who enjoy sports that often use their arms, such as tennis, golf, and badminton, or who repeatedly lift heavy objects.
Trauma such as traffic accidents and falls, incorrect postures and excessive use of shoulders, and lifestyle habits such as smoking can also cause tendon damage in young people. In other words, rotator cuff rupture is not a disease limited to the middle-aged, but a shoulder disease that requires attention at all ages.
Symptoms of rotator cuff rupture are similar to frozen shoulders, calcified tendinitis, and neck disc, which can be easily confused. All can cause severe shoulder pain, but each disease has a different pattern of symptoms. The frozen shoulder is characterized by severe restrictions on the range of passive exercise, and the neck disc is accompanied by radiating pain that extends beyond the shoulder to the lower arm.
On the other hand, rotator cuff rupture causes severe pain when the arm is raised or turned, and muscle strength loss may also occur. As such, shoulder pain can occur for various causes, so accurate differential diagnosis is of paramount importance. If shoulder pain persists for more than two weeks, it is advisable to seek medical attention from an orthopedic surgeon instead of considering it as simple muscle pain or sprains.
If you have pain, it is important to see an orthopedic surgeon and find the exact cause through imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. If diagnosed early, non-surgical treatment such as drug treatment, injection treatment, and rehabilitation treatment can be sufficiently improved. Even if surgery is required, if it is found when the rupture size is small, pain and scarring can be minimized through arthroscopic surgery performed with only a small incision, and the risk of re-destruction is reduced.
After surgery, systematic management such as wearing shoulder aids and rehabilitation exercises is of paramount importance. In particular, long-term rehabilitation and steady exercise habits are essential to prevent stiffness or re-damage of shoulder joints.
The most important thing in rotator cuff rupture is prevention and early diagnosis. It is necessary to keep your shoulder stretching and rotator cuff strengthening exercises consistently, and to maintain the correct posture when lifting heavy objects. In particular, it is desirable for occupational groups or people who enjoy sports who repeatedly use their shoulders to avoid overusing them, and to get enough rest if they feel pain.
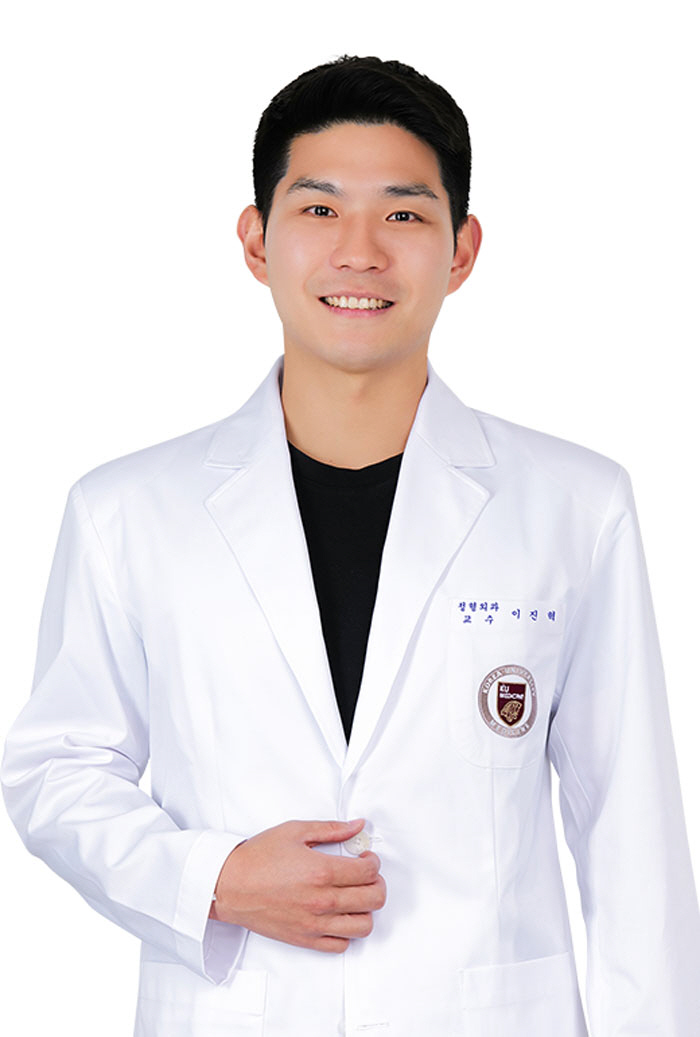
Lee Jin-hyuk, an orthopedic surgeon at Korea University Anam Hospital, advised "If shoulder pain lasts for more than two weeks, it is better not to leave it unattended, but to seek medical attention from an orthopedic specialist" and "We need to keep our shoulders healthy by stretching and exercising strength of strength that suits us normally"
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.