Last year, the total number of food poisoning cases decreased, but the number of salmonella causes increased by 20%
Aug 29, 2025
|
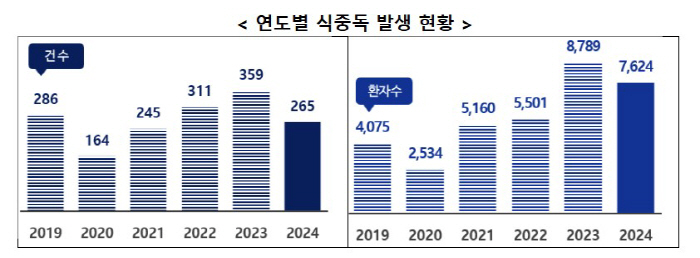
According to the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety's analysis of the food poisoning outbreak in 2024, a total of 265 cases and 7,624 patients were found to have decreased both the number of cases (26%↓) and the number of patients (13%↓) compared to the previous year. Compared to the average of the last three years (about 319 cases, about 6,122) excluding 2020-2021, the number of cases decreased by 17% and the number of patients increased by 25%. However, caution was advised as the number of salmonella food poisoning increased (20% ↑ the number of cases and 25% ↓).
Last year, food poisoning was concentrated in July and September when there was a heat wave and rainy season, and the number of food poisoning cases and patients occurred in restaurants was the highest. In particular, as the number of salmonella food poisoning increases, food ingredients such as eggs and personal hygiene management have become more important.
Looking at the monthly food poisoning trend in 2024, more than 10 cases occurred every month except February, and food poisoning that occurred in summer (July to September) when temperatures and humidity were high accounted for 39% of the total number of cases and 50% of the number of patients. In particular, bacterial food poisoning caused by salmonella and pathogenic E. coli occurred mainly in July and August, when the heat wave continued, and in January and December, when the temperature was low, viral food poisoning such as norovirus was high.
|
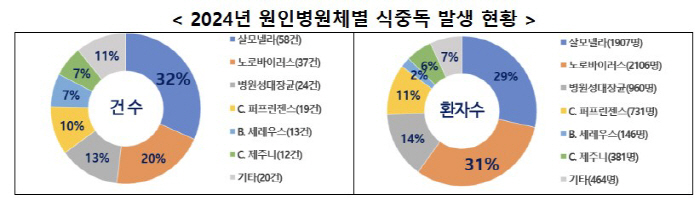
In 2024, 66% (38 cases) of Salmonella food poisoning occurred in restaurants. Salmonella can be cross-contaminated from eggshells to other foods, so wash your hands thoroughly with a detergent after touching eggs, and avoid eating foods suspected of contamination.
Meanwhile, 35% (13 cases) of norovirus food poisoning were found to have occurred in group feeding centers. About 50% (12 cases) of food poisoning with pathogenic E. coli also occurred at the group cafeteria.
Restaurants (154 cases, 2,593 people) were the most common facilities with food poisoning, followed by out-of-school group catering (35, 14245 people) and other facilities (33, 1,831). Due to the development of the food service culture, it occurred mainly in restaurants handling Korean food, raw fish restaurants, and Japanese food, and food poisoning was also found to have occurred a lot in group food service centers such as schools.
Meanwhile, Jeonbuk Special Self-Governing Province had the highest number of food poisoning patients per million population considering the number of people by region at 698, followed by Jeju Special Self-Governing Province at 301 and Gwangju Metropolitan City at 222.
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.