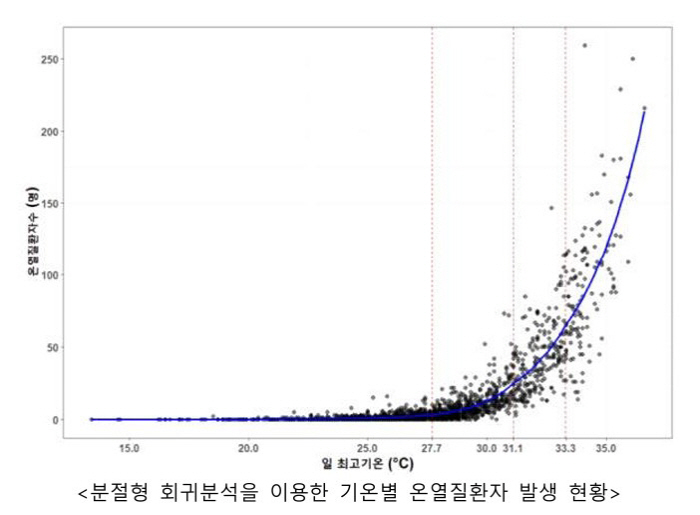
This year, the cumulative number of heat-related diseases is 1.26 times higher than last year…If the maximum temperature is 33.3℃ or higher, more than 50 people occur every 1℃ rise
Aug 22, 2025
|
The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced on the 22nd that it has confirmed a clear correlation between the number of heat-related patients and the maximum temperature.
Since 2011, the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been operating a 'Heat Disease Emergency Room Monitoring System' every year, and about 500 emergency medical institutions nationwide are monitoring the occurrence of heat diseases caused by heat waves and providing major occurrence characteristics information on a daily basis.
This year, the number of heat-related patients exceeded 1,000 at the earliest time since the monitoring system was operated due to the heat wave from the end of June. The cumulative number of patients (as of August 21st) is 3,815, the second highest after 2018 (4393), which was the most intense heat wave since the monitoring of the emergency room for heat diseases in 2011, and 1.26 times higher than the same period in 2024 (3004), which had the second-highest number of heat diseases ever.
As a result of analyzing the data on the emergency room monitoring system for thermal diseases and the daily maximum temperature data for the past 11 years (2015-2025), the occurrence of thermal diseases differed by section according to the temperature increase. Whenever the temperature rose by 1℃, the number of patients with heat illness increased by about 7.4 in the daily maximum temperature range of 27.7℃ to 31.0℃ and by about 22 in the range of 31.1℃ to 33.2℃. In particular, in the section with a daily maximum temperature of 33.3℃ or higher, the increase was found to be rapid, with about 51 people with heat-related diseases occurring every time the temperature rose by 1℃.
As the temperature increases, the number of heat-related patients increases exponentially, and the occurrence of heat-related patients rapidly increases above the daily maximum temperature of 33.3℃, so if high temperatures are predicted, health rules for preventing heat-related diseases must be observed.
Heat illness is an acute disease caused by heat, and symptoms such as headache, dizziness, muscle cramps, fatigue, and loss of consciousness appear when exposed to a high-temperature environment for a long time. If symptoms such as headaches and dizziness appear in hot environments, drink water quickly and move to a cool place to rest. If symptoms do not improve, you should visit the hospital with the help of 119 paramedics and take action.
Lim Seung-kwan, Director of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said "Since the end of June, the number of people with heat-related diseases has increased significantly compared to the past due to early and long-term occurrence of high-temperature environments"Accordingly, we will make preemptive preparations to prevent health damage against heat waves by using temperature data." In addition, he emphasized that "The Korea Meteorological Administration predicts that the daytime temperature at the end of August will be 30~34℃, so it is necessary to continuously comply with health rules for preventing heat diseases."
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.