Dangers of sudden death Quiet hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, how do you handle it normally?
Nov 12, 2025
|
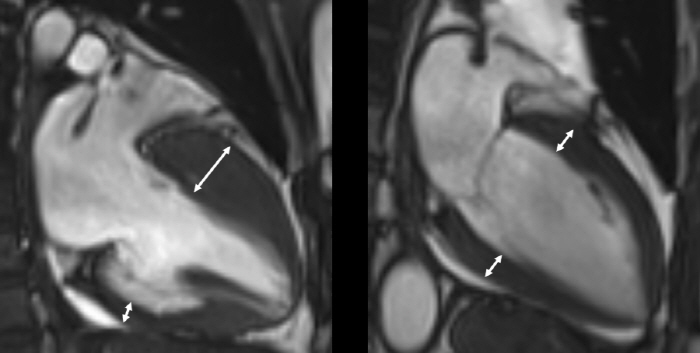
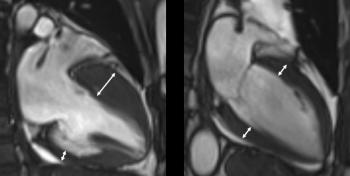
Usually, the myocardium thickens when left unchecked for more than several years, and thickens even when there is aortic valve stenosis, which narrows the outlet of blood from the heart. This is the principle that the heart needs to use more force to release blood, and as a result, muscles develop and thicken. However, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is characterized by excessive thickening of the myocardium without any special reason or even if there is a reason, it cannot be explained to that extent.
The most problematic complication in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is sudden death. In general, there are many cases where there are no symptoms, so it is sometimes diagnosed by fainting or sudden death without any signs of prognosis. Usually, after a medical examination, it is most often confirmed as abnormal electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, and sometimes it is known through a family test on the family history of sudden death.
Diagnosis is made through imaging tests such as echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging, and fibrosis is progressed in the thickened myocardium or muscle tissue is degenerated into adipose tissue. However, as there is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy without such tissue degeneration, comprehensive judgment by a specialist is important.
The goal of treatment for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is to reduce symptoms and prevent complications such as heart failure or sudden death.
Most start with medication to lower heart rate and promote myocardial relaxation. When it is not controlled by drugs, surgical treatment is recommended to secure the path of blood flow by resecting some of the thickened myocardium. In some cases, an irrational procedure that causes partial atrophy of muscles is performed by injecting alcohol into the coronary artery of the ventricular septum. By scoring a history of fainting, a family history of sudden death, the degree of myocardial fibrosis, the presence or absence of ventricular tachycardia, and the degree of myocardial thickening, implantable ventricular defibrillators are also inserted prophylactically in patients with high probability of sudden death.
Since patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can often develop complications such as atrial fibrillation and angina, it is important to detect them early and receive immediate treatment through regular tests even if there are no symptoms.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients in high-risk groups due to personal or family history are at risk of sudden death due to arrhythmia, but most patients can safely maintain their daily lives through proper management and regular examination. Low and medium-intensity exercises such as walking, yoga, and light cycling can help cardiovascular health. However, since high-intensity exercise exceeding 70% of the maximum heart rate lacks safety evidence, it is desirable to increase the strength step by step through sufficient inspection and pre-evaluation.
"As hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can lead to sudden death in high-risk groups, it is important to detect and manage it early through regular examinations if you have a family history or fainting history," said Kim Yong-hyun, a professor of circulatory technology at Korea University Ansan Hospital. "It is important for guardians to learn how to use CPR and automatic defibrillators in preparation for sudden death situations."
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.