Development of New Technology for Reconstruction of Skin Cancer Using Nano Fat...Heals fast, less scar contraction
Mar 10, 2025
A research team led by Han Seung-gyu, a professor of plastic surgery at Korea University Guro Hospital, has developed a new skin cancer regeneration technology that has a fast regeneration rate, has low scar contraction, and minimizes facial deformation.
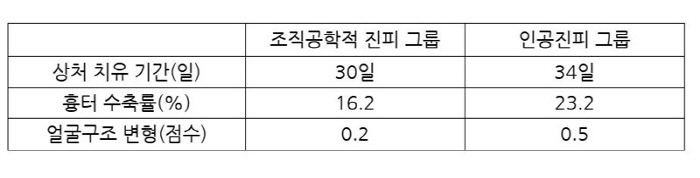
Using a new technology that transplants tissue-engineered dermis using cells in the patient's adipose tissue to regenerate the skin cancer removal site, scar contraction was 30% less than using the existing artificial dermis, and healing speed was faster.
Skin cancer is the most common malignant tumor and its incidence is increasing worldwide, and according to data from the Central Cancer Registry, the number of new skin cancer patients in Korea was 8,135 in 2022, accounting for 2.9% of all cancer cases. Skin cancer is mainly related to ultraviolet exposure and often occurs in exposed facial areas, especially in the elderly. Unlike other cancers, skin cancer rarely metastasizes, so it is often treated with surgical resection alone, so reconstruction of the resected area is necessary.
To reconstruct the skin cancer resection site, local sheath surgery or autologous skin transplantation is used. However, because these methods are accompanied by a complex surgical process, the surgical burden is high for elderly patients. In addition, in the case of local epithelium, additional surgery is required because it can cause scars or facial structure deformation, and in the case of autologous skin transplantation, scars and pain in the skin collection area are inevitable in addition to facial scars. Recently, artificial dermis has been used to improve these shortcomings, but it is difficult to completely prevent scar contraction, so there were limitations in cosmetic areas due to the nature of skin cancer issued to exposed areas such as the face.
To overcome the limitations of existing treatments, Professor Han's research team developed a method to reconstruct the skin cancer removal area by minimizing scar contraction or deformation using nano-fat (fine fat). After local anesthesia, about 7-10ml of fat tissue is collected from the patient's abdomen, crushed into nano-fat using a microcrushing device, and mixed with artificial dermis to make a 'nano-fat tissue engineering dermis' and transplanted into the defect area. Nanofat contains cell components such as stem cells, collagen, and growth factors, which promote wound regeneration and minimize scarring.
A comparative analysis of the effect of the nano-fat tissue engineered dermis developed by the research team showed that the nano-fat tissue engineered dermal transplant group had four days faster wound healing and less scarring than the existing artificial dermal transplant group, especially with about 30% less scarring. In addition, when existing artificial dermis is transplanted, facial structure deformation may occur, but patients who transplanted tissue engineering dermis have much fewer such deformation, which is effective in maintaining the facial contour naturally.
Professor Han Seung-gyu said "This study confirmed that the use of tissue engineering dermis using nano-fat is effective in reducing scarring and facial deformation. In particular, in the use of cell therapy that promotes regeneration, the procedure can be performed in 20 minutes without complicated procedures such as cell culture, so it is expected to be easy to apply clinically and become a standard treatment for reconstruction after skin cancer in the future"We plan to expand research so that the tissue engineering dermis using nano-fat can be applied to other skin damage treatments through continuous research activities in the future."
On the other hand, this research paper 'Compareison of Tissue-Engineered Dermis with Micronized Adipose Tissue and Artificial Dermis for Facial Reconstruction Skin Cancer Reservation' was published in the latest issue of Bioengineering'Bioengineering', an international academic journal in the field of bioengineering and regenerative medicine.
Using a new technology that transplants tissue-engineered dermis using cells in the patient's adipose tissue to regenerate the skin cancer removal site, scar contraction was 30% less than using the existing artificial dermis, and healing speed was faster.
Skin cancer is the most common malignant tumor and its incidence is increasing worldwide, and according to data from the Central Cancer Registry, the number of new skin cancer patients in Korea was 8,135 in 2022, accounting for 2.9% of all cancer cases. Skin cancer is mainly related to ultraviolet exposure and often occurs in exposed facial areas, especially in the elderly. Unlike other cancers, skin cancer rarely metastasizes, so it is often treated with surgical resection alone, so reconstruction of the resected area is necessary.
To reconstruct the skin cancer resection site, local sheath surgery or autologous skin transplantation is used. However, because these methods are accompanied by a complex surgical process, the surgical burden is high for elderly patients. In addition, in the case of local epithelium, additional surgery is required because it can cause scars or facial structure deformation, and in the case of autologous skin transplantation, scars and pain in the skin collection area are inevitable in addition to facial scars. Recently, artificial dermis has been used to improve these shortcomings, but it is difficult to completely prevent scar contraction, so there were limitations in cosmetic areas due to the nature of skin cancer issued to exposed areas such as the face.
To overcome the limitations of existing treatments, Professor Han's research team developed a method to reconstruct the skin cancer removal area by minimizing scar contraction or deformation using nano-fat (fine fat). After local anesthesia, about 7-10ml of fat tissue is collected from the patient's abdomen, crushed into nano-fat using a microcrushing device, and mixed with artificial dermis to make a 'nano-fat tissue engineering dermis' and transplanted into the defect area. Nanofat contains cell components such as stem cells, collagen, and growth factors, which promote wound regeneration and minimize scarring.
A comparative analysis of the effect of the nano-fat tissue engineered dermis developed by the research team showed that the nano-fat tissue engineered dermal transplant group had four days faster wound healing and less scarring than the existing artificial dermal transplant group, especially with about 30% less scarring. In addition, when existing artificial dermis is transplanted, facial structure deformation may occur, but patients who transplanted tissue engineering dermis have much fewer such deformation, which is effective in maintaining the facial contour naturally.
Professor Han Seung-gyu said "This study confirmed that the use of tissue engineering dermis using nano-fat is effective in reducing scarring and facial deformation. In particular, in the use of cell therapy that promotes regeneration, the procedure can be performed in 20 minutes without complicated procedures such as cell culture, so it is expected to be easy to apply clinically and become a standard treatment for reconstruction after skin cancer in the future"We plan to expand research so that the tissue engineering dermis using nano-fat can be applied to other skin damage treatments through continuous research activities in the future."
On the other hand, this research paper 'Compareison of Tissue-Engineered Dermis with Micronized Adipose Tissue and Artificial Dermis for Facial Reconstruction Skin Cancer Reservation' was published in the latest issue of Bioengineering'Bioengineering', an international academic journal in the field of bioengineering and regenerative medicine.
|
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.