Male Octopus Poisoning Females Before Mating...I'm not going to get eaten
Mar 13, 2025
|
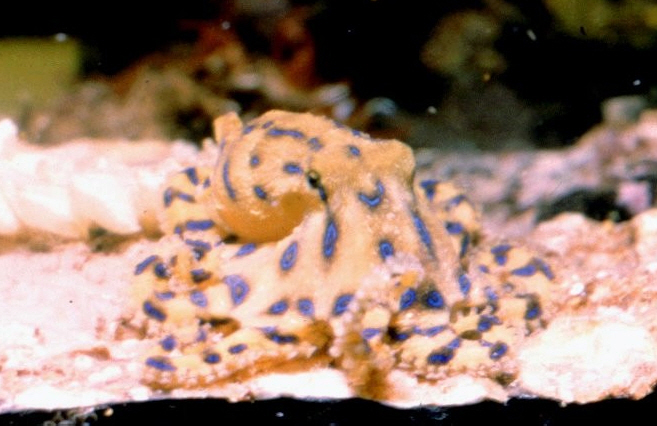
Researchers at the University of Queensland in Australia stated that `Males of blue trout inject a poison called tetrodotoxin into females and are not eaten during mating.'
In general, females of blue trout are about twice as large as males. It is known to tend to prey on males given the opportunity.
The male sedates the female by injecting tetrodotoxin, a deadly poison found in pufferfish.
When the researchers observed octopus mating in the laboratory, the male added tetrodotoxin to the female's aorta, and the female paralysed by the venom became pale in skin, decreased respiratory rate, and slow in movement.
The male has been mating in the meantime, and when the toxin disappeared, the female pushed the male away.
None of the females observed in the laboratory died from the poisoning. This suggests that females have some resistance to toxins, the researchers explained. However, after mating, the female was found with swollen bumps and torn wounds. All females observed in the study laid eggs within 3 to 29 days.
Regarding the venom, the researchers say it is derived from symbiotic bacteria living inside the octopus' body, not from the octopus itself," he said.
The findings were recently published in the international journal 『Current Biology』.
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.