Blood sugar control for diabetic patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass surgery, and real-time continuous blood glucose meter is useful
Apr 11, 2025
|
Professor Kwak Soo-heon and Professor Son Hee-joon of the Department of Endocrine Metabolism at Seoul National University Hospital and Professor Hwang Ho-young and Son Seok-ho of Cardiovascular Thoracic Surgery announced the results of a study on the 11th that confirmed the effect of continuous blood glucose meters and remote monitoring on type 2 diabetes patients who underwent coronary artery bypass surgery.
Coronary artery disease is a fatal disease that causes angina or myocardial infarction as the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle narrow. To this end, we receive coronary artery bypass, which creates a new bypass that will supply blood flow to the heart. One in three people undergoing this operation is type 2 diabetes, who have a worse risk of coronary artery disease than the general population. In particular, if blood sugar is not well controlled after surgery, the mortality rate and the risk of atrial fibrillation, infection, and lung complications can be increased, so effective blood sugar control methods were needed.
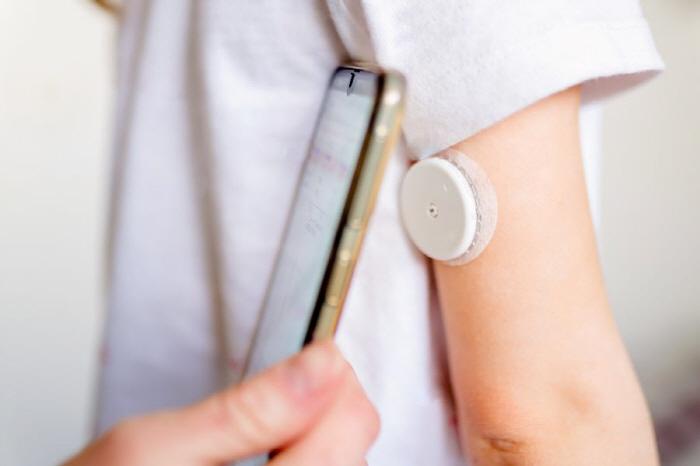
The research team paid attention to a continuous blood glucose meter (CGM) that automatically collects and transmits real-time blood glucose information 24 hours a day. Using this device makes it easy to manage blood sugar and can respond quickly to rapid changes in blood sugar.
The team randomly assigned patients with type 2 diabetes who were admitted to the ward after coronary artery bypass surgery to the test group (48) and the control group (43). The test group was remotely monitored by wearing a real-time continuous blood glucose meter, and the control group used a field-diagnosed blood glucose meter four times a day.
As a result of correcting age, sex, BMI, fasting blood sugar, and glycated hemoglobin, the maintenance time of target blood sugar (70-180 mg/dL) was significantly longer in the test group than in the control group (60.3% vs. 50.3% on average). In addition, the test group had significantly lower average blood sugar compared to the control group, and the target blood sugar excess time was also short.
On the other hand, there is no difference in the frequency of hypoglycemic events (with less than 70 mg/dL lasting more than 15 minutes) between the two groups, indicating that the use of a continuous blood glucose meter can provide a safe treatment environment without causing additional hypoglycemic risk to diabetic patients after coronary artery bypass.
The research team explained that this result is because insulin administration can be performed in a timely manner using continuous blood glucose meters and remote monitoring, enabling optimized blood sugar control.
Professor Kwak Soo-heon (International Medicine of Endocrine Metabolism) "This study confirmed that the combination of continuous blood glucose meter and remote monitoring is an effective way to improve the surgical prognosis of diabetic patients hospitalized after heart surgery by enabling individualized blood glucose management."We will continue our study to confirm the effectiveness of continuous glycemic meter in various surgical environments as well as later coronary artery bypass."
Meanwhile, the study was conducted with Korean-style family donation research funds and was published in the recent issue of 「Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism」.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.