Quiet joint destruction, rheumatoid arthritis...Treatment and prevention?
Jul 06, 2025
|
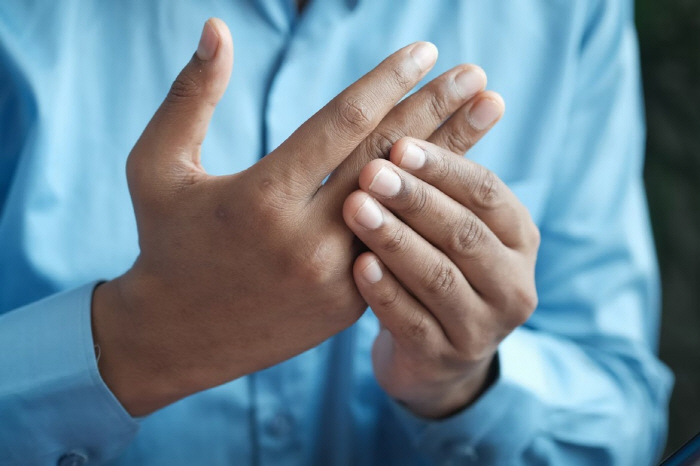
Although the exact cause of the outbreak is not clear, rheumatoid arthritis is a representative autoimmune disease caused by abnormalities in the immune system. The inflammatory reaction begins when lymphocytes, which need to defend against bacteria or viruses invading from the outside, attack the active membrane surrounding their joints.
When the synovial is inflamed, various white blood cells, including lymphocytes, flock to the joint area, and the joint fluid increases abnormally, causing swelling and pain in the joint. If symptoms persist, abnormally proliferated inflammatory synovial tissue can invade cartilage and bones, leading to deformation and dysfunction such as bending or hardening of joints.
Kang Eun-song, a professor of rheumatology at Korea University Ansan Hospital, said "In the past, joints were stiff and daily life was difficult due to rheumatoid arthritis, but recently, treatments have developed a lot."If treatment is started early, you can live without major problems for the rest of your life while effectively controlling inflammation."
The most basic treatment is control of inflammation and pain using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroid preparations. However, these drugs only temporarily relieve symptoms and have limitations in preventing the progression of the disease. Therefore, in the long run, it is necessary to regulate the immune response itself through immunomodulatory drugs such as antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biological agents.
Classical antirheumatic preparations include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine, and if it does not work, leflunomide or tacrolimus, a calcineurin inhibitor, is used.
These formulations can take months to take effect, and side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, headache, and rash can occur.
Recently, biological agents have been widely used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. It is designed to inhibit specific target substances involved in the development of autoimmune diseases, i.e., related cytokines (protein immunomodulators secreted from immune cells) and cells.
It is used when there is no response to classical antirheumatic agents, and the effect appears quickly. Biological agents approved to date are largely anti-cytokine inhibitors, T-cell inhibitors, and B-cell inhibitors.
Professor Kang "Currently actively utilizes various biological agents to provide customized treatment tailored to each patient's disease characteristics and response, and as a result, many patients are preventing joint damage and showing good progress."If early treatment is late, steady management can slow progress and prevent joint deformation and dysfunction, so it is necessary to receive active treatment in consultation with a specialist."
Balanced self-management throughout daily life is also important for effective management of rheumatoid arthritis. In particular, in order to maintain joint function and prevent muscle atrophy, it is recommended to continue low-intensity exercise such as stretching, walking, and underwater exercise within the range that does not strain the joint. In addition, maintaining a balanced diet containing various nutrients and securing sufficient rest and sleep time helps to control general health and pain.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.