Determination of Genetic Causes of Slow and Hardening Teeth Growth
Aug 19, 2025
|
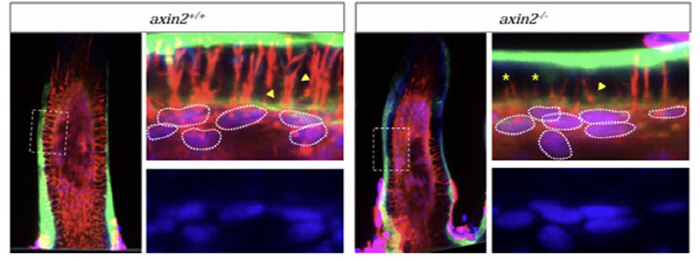
A research team led by Professor Park Hae-cheol and Professor Shim Ji-seok of the Department of Dental Medicine at Korea University analyzed precisely what changes occur when there is no gene called Axin2 with a zebrafish experimental model. The Axin2 gene is responsible for the Wnt signaling pathway that coordinates the development of cells and organs. The Wnt signaling pathway is a transmission channel that tells cells when and how to grow, and is essential for the development of various organs such as teeth and bones.
The research team found that zebrafish, which removed the Axin2 gene through gene editing technology (CRISPR/Cas9), not only reduced body size but also delayed the time when teeth grew. The amount of calcium and phosphorus, which are inorganic components needed to harden teeth, has been significantly reduced. In addition, the activity of key genes for making teeth has also slowed down.
The study shows that the Wnt signal must work in a timely manner in order for a tooth to become healthy and firm. If this signal is not properly controlled due to genetic problems, it can make the teeth soft or slow down their growth.
Professor Shim Ji-seok of the dental school at Korea University Medical School said, `The results of this study can be a key clue for understanding the cause of hereditary dental diseases"It will be an important basis for future tooth regeneration and treatment research," he stressed.
On the other hand, the study was published in the 2025 edition of the Journal of Dental Research, a world-renowned journal of dentistry, under the title 'Axin2 Deficiency Causes Hyponominalization and Delayed Tooth Development'.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.