deterioration of cardiovascular diseases such as periodontal diseases, hypertension, and arteriosclerosis
|
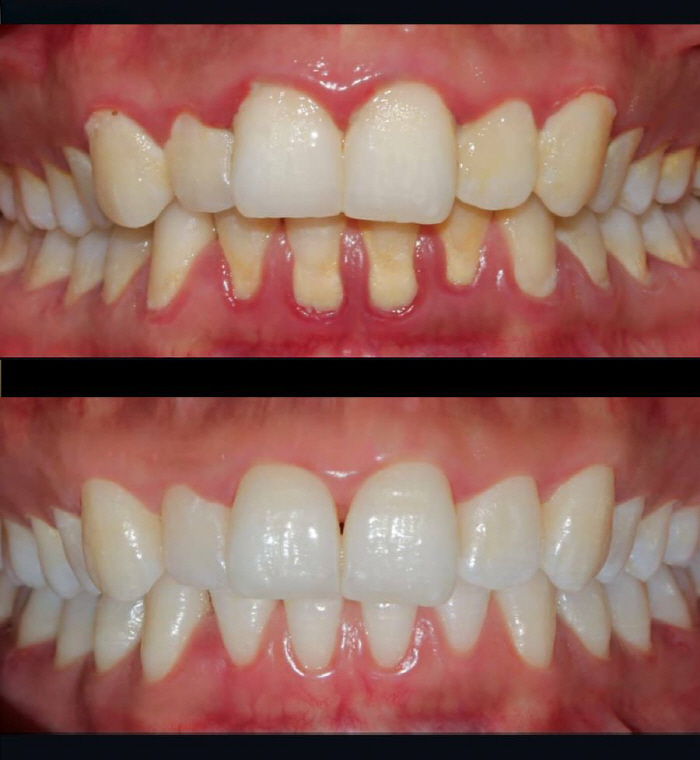
According to statistics from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, since 2019, the number of patients with 'gingitis and periodontal disease' has pushed out acute bronchitis, which has always been the number one, and has taken the most common 'ing disease'ing place in Korea. This means that more patients visit hospitals for gum disease than colds. Periodontal disease refers to diseases that appear not only in the red gums surrounding the teeth, but also in tissues that support the teeth under them (gum bones, chalk, periodontal ligament). It is often divided into gingivitis and periodontitis, and it is only lightly bleeding in the early stages, but severe chronic periodontitis, which is often called 'Pungchi', is a scary disease that causes gum bones to melt, shake teeth, and in severe cases, lose teeth.
Periodontal disease is not just a matter of oral health. In particular, it should not be overlooked that periodontal disease is associated with various systemic non-infectious chronic diseases. About 700 species, hundreds of billions of bacteria are distributed in the oral cavity, and the gums have a high distribution of blood vessels, making it easy for bacteria to enter the blood vessels. In particular, the gap between the teeth and the gums is one of the few unique structures in our body, where hard hard and soft tissues are in contact. This area, where tissues with completely different properties are joined, forms a hard physical barrier if normal, but when exposed to persistent inflammation, it may be the first weakness area where bacterial penetration occurs.
P. gingivalis, a representative periodontitis-causing bacterium, and its toxins enter through a gum gap called 'periodic sac' and move along the bloodstream, stimulating vascular endothelial cells. If these chronic inflammatory stimuli persist for a long time, atherosclerotic plaque may form on the inner wall of blood vessels. The atherosclerotic plaque is a mass that narrows blood vessels and can interfere with blood flow, worsening cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure, ischemic heart disease, and arteriosclerosis.
In addition, severe periodontal inflammation stimulates the immune system, increasing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and causing insulin resistance, making it difficult to control blood sugar. Recently, toxins derived from P. gingivalis, such as LPS and gingipain, have been identified in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, suggesting that pathogenic substances can pass through the cerebrovascular barrier along the bloodstream and cause progressive dementia or amyloid deposition.
|
The most commonly recommended method is 'modified Bath method', which is effective in preventing gingivitis and periodontitis. The important point is that the toothbrush hair is placed at a 45-degree angle on the border between the gums and teeth, and then it focuses on cleaning the teeth and gum boundaries called 'dental sac' in a way that vibrates finely. In addition, there are many studies showing that brushing alone removes only about 30-60% of the total dental plaque in the oral cavity. Therefore, for effective oral hygiene management, auxiliary devices such as dental floss, interdental toothbrushes, and mouthwash must be used together.
Professor Kim Hyun of dental dentistry at Korea University Ansan Hospital explained, "It is important not to miss brushing your teeth before going to bed because the secretion of saliva is reduced during sleep, and bacterial activity is the most active during sleep." "Since the pH in the mouth temporarily decreases immediately after eating acidic food, the surface layer of the teeth is finely corroded, it is recommended to rinse thoroughly with water and brush after 30 minutes."
Periodontal inflammation is a disease in which patients and doctors must establish a trust relationship and manage it regularly rather than 'completion'. Regular inspection and scaling are recommended at least every six months even if there are no abnormalities, and regular inspection every three months is recommended for patients with severe periodontitis, poor oral habits, poor prosthetics, or uncontrolled chronic diseases.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.