Predicting Biological Age and Health Risk with AI...Seoul National University Hospital, Naver Develops AI Model
Nov 07, 2025
|
Biological Age (BA) is a numerical expression of the actual degree of aging of the body by combining various factors such as genetics, lifestyle, environment, and disease history. A lower biological age than the actual age (CA) means a good health condition, and a higher age can lead to faster aging or higher disease risk. However, existing biological age prediction models were mainly based on data from healthy people, making them difficult to apply to chronically ill patients and not reflecting the risk of death.
The team of professors Cho Young-min, Bae Jae-hyun, and Yoon Ji-wan of the Department of Endocrine Metabolism at Seoul National University Hospital, and Dr. Yoo Han-joo and Moon Sung-eun of Naver Digital Healthcare LAB analyzed data from 151,281 people who received medical checkups at Seoul National University Hospital's Gangnam Center from 2003 to 2020. The data included physical measurements, blood and urine tests, lung function tests, disease presence and death information, and the study subjects were classified into the ▲ normal group ▲ pre-disease group ▲ disease group according to blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol (lipid) levels.
Based on this data, the research team designed an AI model with a transformer structure. AI predicts an individual's biological age (BA) by integrating various health indicators such as blood pressure, blood sugar, lung function, and cholesterol, and compares them with the actual age (CA) to calculate the difference between the two values (BA-CA gap). Based on large-scale learned data, AI analyzes whether the user's health indicators are similar to the group with high survival rates in the past or the group with high risk of death and presents specific predictions.
In addition, gender-specific models were trained respectively to reflect physiological differences between men and women, and AI also learned how changes in health indicators affect disease presence and mortality risk. Through this, we have completed a model that can evaluate the statistical association of current health conditions with future survival rates, not just calculating biological age.
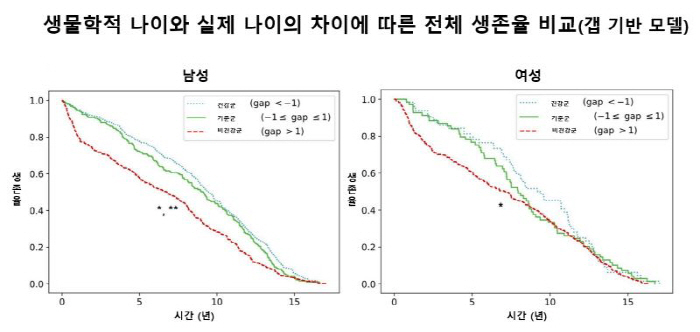
As a result of the analysis, the newly developed AI model clearly distinguished the normal group, the pre-disease group, and the disease group. In the normal group, the biological age was lower than the actual age (BA < CA) and the disease group was higher (BA > CA), showing a distinct difference according to health status. The BA-CA gap widened as blood sugar, blood pressure, and lipid levels worsened, and this gap increased significantly even in the presence of cardiovascular disease or cancer.
Based on the BA-CA value calculated by AI, the research team performed Kaplan-Meier survival analysis by dividing it into ▲health group (BA-CA < -1) ▲ reference group (-1≤BA-CA≤1) ▲non-health group (BA-CA > 1).
|
On the other hand, conventional biological age prediction models (Klemera&Doubal's Method, Chronological Age Cluster, Deep Neural Network) have not consistently distinguished these differences.
Professor Cho Young-min (Endocrine Metabolism) stated, "This study is significant in that it is the first transformer-based biological age prediction model to learn disease prevalence and death information at the same time. "AI has evolved beyond simply calculating biological age into a new clinical tool that can reflect an individual's health status and future risks together."
He added that "'The large-scale clinical data of Seoul National University Hospital and Naver's advanced AI technology are combined to representative achievements of industry-academia cooperation created by medical expertise and technology.'"
The results of this study were published in the recent issue of the international journal 『Journal of Medical Internet Research』 in the field of medical informatics.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.