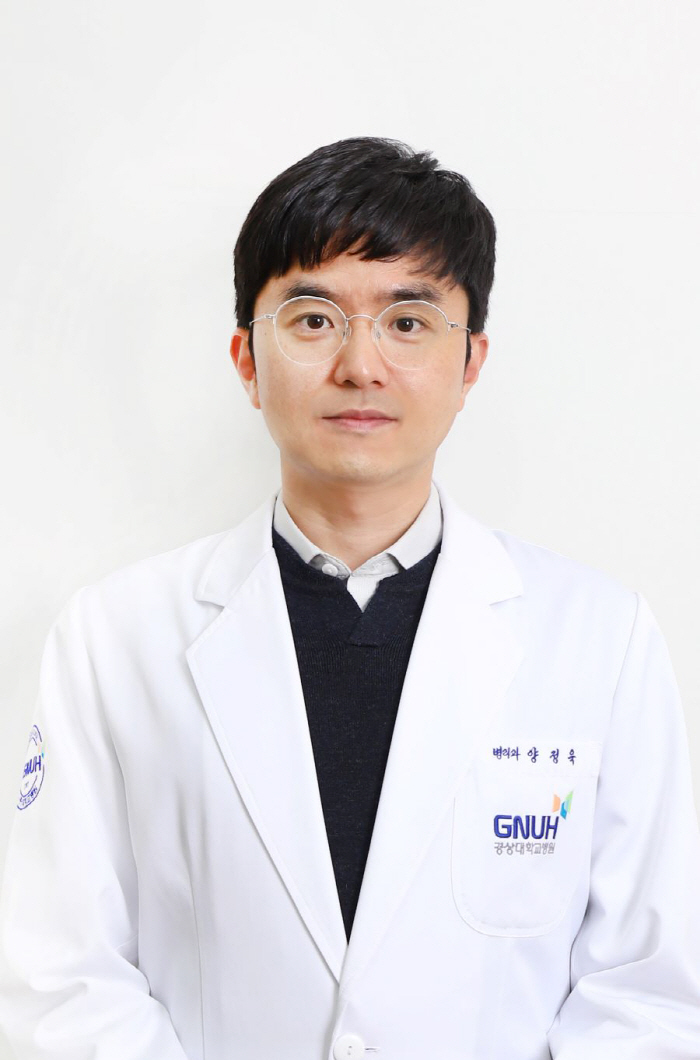
Professor Yang Jung-wook's research team at Gyeongsang National University Hospital, published in international renowned journals, and selected BRIC Hanbit Corporation
Nov 05, 2025
Gyeongsang National University Hospital (Hospital Director Ahn Sung-ki) reported that a research team led by Professor Yang Jung-wook of the Department of Pathology was published in the Nature Partner Journal 'npj Digital Medicine (IF 15.1)' on the 14th of last month.
The paper was also selected by the Center for Biological Research and Information (BRIC) 'People Who Shined Korea (abbreviated as Hanbitsa)' to select and introduce Korean researchers who published papers in world-renowned journals in life science.
The title of the paper is 'Evidental deep learning-based ALK-expression screening for ALK expression screening using H&E pathological tissue slides' and is a study that predicts ALK gene expression by analyzing lung cancer tissue slides (H&E) images with a deep learning-based artificial intelligence model.
About 3% to 5% of non-small cell lung cancers have abnormalities in the ALK gene, and the survival rate is significantly improved when ALK-targeted treatment is applied to ALK-positive patients. However, more than 95% of patients are judged 'negative' in the ALK companion diagnostic test results, so most of them can be seen as meaningless consumption of test costs and specimens.
The deep learning model 'DeepPATHO' developed by Professor Yang Jung-wook's research team predicted ALK expression with more than 95% accuracy with only existing H&E staining slides. This was the first time that it showed good enough performance to be applied to actual clinical practice, and its performance was also confirmed in surgical and small biopsy specimens.
In particular, we presented a prediction basis consistent with existing pathological knowledge by visualizing and displaying which areas of the tissue artificial intelligence (AI) predicted. This differs from existing studies in that it is a technology that secures not only accuracy but also explainability of prediction results.
If a companion diagnostic test is performed only when ALK positive is predicted using the technology of this study, it is expected that the cost of testing and sample consumption wasted on meaningless tests can be reduced. In addition, when the amount of samples is small, samples can be efficiently used by prioritizing ALK tests on samples predicted to be ALK positive among several genetic tests.
Professor Yang Jung-wook said, "We plan to verify the performance of predicting ALK expression in various hospitals and slide scanner environments in the future. In addition, we will continue the research to expand the research area such as predicting other treatment targets, patient treatment response and prognosis so that it can be used for actual clinical diagnosis." he said.
The paper was also selected by the Center for Biological Research and Information (BRIC) 'People Who Shined Korea (abbreviated as Hanbitsa)' to select and introduce Korean researchers who published papers in world-renowned journals in life science.
The title of the paper is 'Evidental deep learning-based ALK-expression screening for ALK expression screening using H&E pathological tissue slides' and is a study that predicts ALK gene expression by analyzing lung cancer tissue slides (H&E) images with a deep learning-based artificial intelligence model.
About 3% to 5% of non-small cell lung cancers have abnormalities in the ALK gene, and the survival rate is significantly improved when ALK-targeted treatment is applied to ALK-positive patients. However, more than 95% of patients are judged 'negative' in the ALK companion diagnostic test results, so most of them can be seen as meaningless consumption of test costs and specimens.
The deep learning model 'DeepPATHO' developed by Professor Yang Jung-wook's research team predicted ALK expression with more than 95% accuracy with only existing H&E staining slides. This was the first time that it showed good enough performance to be applied to actual clinical practice, and its performance was also confirmed in surgical and small biopsy specimens.
In particular, we presented a prediction basis consistent with existing pathological knowledge by visualizing and displaying which areas of the tissue artificial intelligence (AI) predicted. This differs from existing studies in that it is a technology that secures not only accuracy but also explainability of prediction results.
If a companion diagnostic test is performed only when ALK positive is predicted using the technology of this study, it is expected that the cost of testing and sample consumption wasted on meaningless tests can be reduced. In addition, when the amount of samples is small, samples can be efficiently used by prioritizing ALK tests on samples predicted to be ALK positive among several genetic tests.
Professor Yang Jung-wook said, "We plan to verify the performance of predicting ALK expression in various hospitals and slide scanner environments in the future. In addition, we will continue the research to expand the research area such as predicting other treatment targets, patient treatment response and prognosis so that it can be used for actual clinical diagnosis." he said.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.