High-level knee replacement, robotic surgery to increase accuracy...shorten operation time at Himchan Hospital and reduce bleeding by 30%
Apr 17, 2025
|
Partial knee replacement is a treatment that can be performed when the cartilage inside the knee is partially damaged, and only about two-fifths of the joints are changed to artificial joints and normal joints are preserved as much as possible. There are many advantages because it minimizes damage to normal tissue, but it has not been commonly performed in Korea due to the high difficulty of surgery. This is because it is difficult to secure visibility because the incision is small, so it is difficult to balance the insertion position, angle, and ligament of the artificial joint.
To compensate for these limitations, as more and more hospitals use robotic surgical instruments, Himchan Hospital's Arthology Research Institute conducted a comparative study on the effectiveness of partial robotic replacement surgery.
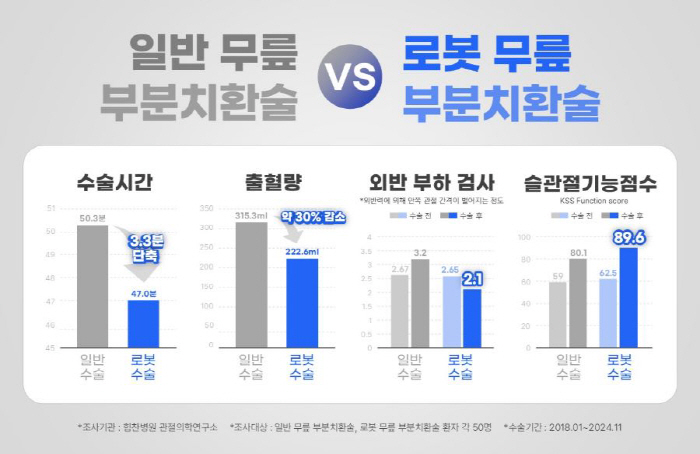
According to a survey of 50 patients with general surgery and robotic surgery among knee partial replacement surgery, the average operation time decreased by 3.3 minutes to 50.3 minutes for general surgery and 47 minutes for robotic surgery. Shortening the operation time reduces the risk of infection or complications as a number of variables are reduced. In general, the higher the proficiency of the surgeon and the better the teamwork of the surgical team, the less surgery time can be.
The amount of bleeding decreased by about 30% to 315.3 ml for general surgery and 222.6 ml for robotic surgery. Bleeding is also a major factor in infections and complications.
An external load test that measures how wide the inner joint gap widens (JLCA) according to the external reaction force pushed from the outside of the knee while the patient is standing can determine that the smaller the angle, the more stable the knee joint. As a result of the investigation, it was found that the knee joint was more stable after robotic surgery at 2.1 degrees and general surgery at 3.2 degrees.
As for the axis of the leg, robotic surgery was more straight. Robotic surgery was 2.7 degrees and general surgery was 3.6 degrees, and robotic surgery was corrected 0.9 degrees more correctly. The KSS Function Score, which evaluates joint function by walking distance, the degree of use of stairs, and the use of a cane or crutches, was also higher in robotic surgery (89.6 points) than in general surgery (80.1 points).
Lee Soo-chan, CEO of Himchan Hospital (Orthopedic Surgeon), said "As a result of conducting clinical research on more than 590 partial knee replacements using robotic surgical instruments so far, it has been confirmed that there is a significant effect in operation time, amount of bleeding, stability of knee joints, and correction angle."In particular, for knee artificial joint surgery using Mako and Rosa, which are competing for the lead in the domestic artificial joint surgery robot market, the success rate of partial replacement will be further increased based on their high proficiency in robotic surgery."
However, a thorough examination and specialist consultation are essential because partial replacement can only be considered if the inside of the knee cartilage is damaged, the function of the cruciate ligament is normal, there is no pain in the outer area, and the O-shaped leg deformation is within 10 degrees.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.