Development of natural capsaicinoid synthetic biological process technology with only enzymes...It opens the way for high-efficiency production of anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, and pain-effect substances
Oct 24, 2025
|
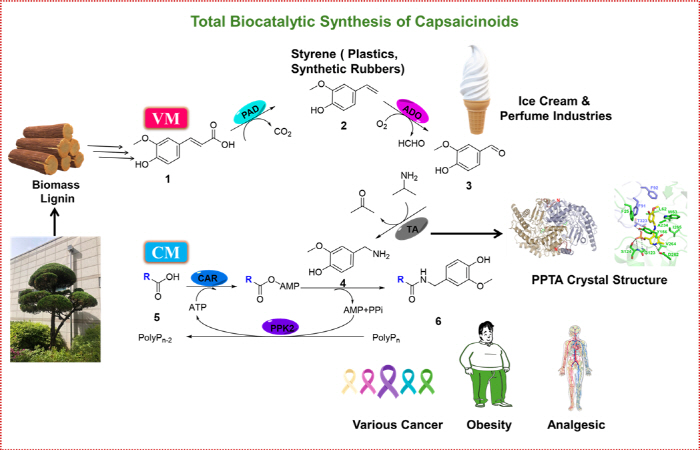
Capsaicinoid contains capsaicin, a spicy component of peppers, and is a natural product with various physiological activities such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anti-obesity, and is widely used in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics industries. However, conventional chemical synthesis methods have many side reactions and high environmental burdens, and existing metabolic pathways of microorganisms have low efficiency, making it difficult to produce high efficiency.
Through a synthetic biological approach, the joint researchers designed a new biosynthetic pathway and discovered the optimal enzymes needed for it to establish an efficient biological process.
The biological process developed by the researchers consists of a two-stage enzyme module system using ferulic acid as a starting material. In the first 'vanillia module', phenolic acid decarboxylase, aromatic diatase, and transaminase were linked to convert ferulic acid to vanillamine. In the second 'capsycinoid synthesis module', vanillamine and fatty acids were combined using the amination reaction of carboxylic acid reductase, and ATP was regenerated through polyphosphate kinase to increase the energy efficiency of the enzyme reaction.
In addition, vanillin and vanillamine intermediates produced in the synthesis path are high-value-added compounds that can be used as flavoring and pharmaceutical raw materials, further enhancing the industrial scalability and applicability of this process.
In this study, Professor Yoon Hyung-don's research team conducted the design of synthetic pathways, the discovery of highly active enzymes, and the development of bioconversion processes. Professor Yong-seok's research team was in charge of analyzing the structure of the core enzyme, transaminase, and identifying the reaction mechanism, while Professor Geum Young-soo's research team carried out precise verification through mass analysis of the product compound.
Dr. Taresh Kobragade of Konkuk University's Department of System Biotechnology participated in this study as the first author, Professor Yun Hyung-don and Professor Yong-seok were the corresponding authors, and Professor Geum Young-soo participated as co-authors.
Meanwhile, this study was carried out with the support of the Korea Research Foundation's Basic Science Research Support Project, Bio-Medical Technology Development Project, and Petroleum Alternative Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project.
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.