Development of AI-based treatment appropriate dose prediction model...There's less error with a specialist's prescription
Nov 21, 2025
|
Professors Song Kyung-chul and Kim Joon-young of Yonsei University's Gangnam Severance Hospital, Ko Tae-hoon of the Catholic University of Medicine's medical informatics class, and Dr. Lee Kang-hyuk's research team recently successfully developed and verified the effectiveness of an artificial intelligence-based model that predicts the optimal dose of the treatment 'methimazole' used for children and adolescent hyperthyroid patients.
Hyperthyroidism in childhood and adolescence is a disease in which thyroid hormones are secreted excessively and the metabolic rate increases abnormally. It causes physical and mental problems such as growth disorders and poor academic performance in growing children, and in serious cases, it can lead to threatening complications such as thyroid poisoning seizures, so early diagnosis and treatment are very important.
The primary treatment for hyperthyroidism in children and adolescents is 'Methimazole'. Since it is administered for a long time, there is a risk of serious side effects such as hypothyroidism, hepatotoxicity, and leukopenia if dose errors occur. Therefore, precise dose setting is the core of treatment, but there is a lack of objective predictive means for appropriate drug doses, forcing them to rely only on the clinical experience of medical staff.
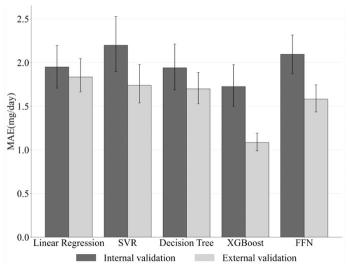
The research team analyzed a total of 2,209 cases of pediatric and adolescent patient data from three institutions: Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yongin Severance Hospital, and Konyang University Hospital. The research team trained various machine learning models, including linear regression, decision tree, support vector regression, XGBoost, and feedforward neural networks, using patients' body measurement information such as age, gender, height, and weight, thyroid function test results at current and immediate visits, and past methimazole prescription doses.
Our results show that the XGBoost model performs best in both internal and external validation. In particular, the external data verification of the XGBoost model showed only a dose prescribed by an experienced specialist and an average error of 1.08mg (MAE). This figure is only one-fifth of the dose of 5 mg, which is the minimum unit of administration, methimazole. Considering that the average methimazole dose of pediatric and adolescent patients who participated in the study is about 8 mg, it corresponds to a very low error rate. This suggests the high accuracy of AI-based models and is evaluated to be immediately available as a clinical decision support tool.
The research team visualized and quantified the variables that have the greatest impact on model prediction by applying the SHAP (Shapley Additive exPlanations) analysis technique to ensure transparency in artificial intelligence-based prediction models. SHAP is a technology that measures and explains the contribution of each factor to what data a complex artificial intelligence made when predicting a specific outcome
The variables that have the greatest impact on model prediction were in the order of 'pre-prescription dose', 'free T4 hormone', and 'blood T3 hormone', confirming that the AI model effectively learned the decision-making process in real clinical practice.
This study is of great academic significance in that it developed the world's first data-based artificial intelligence drug dose recommendation model and verified its effectiveness in the treatment of hyperthyroidism in children and adolescents. In particular, it is expected to open a new trend of precision medical care in the pediatric field by presenting the possibility of an artificial intelligence model that helps the precision of drug administration in a group of children and adolescents whose metabolism and effectiveness are very variable unlike adults.
Professor Song Kyung-chul "Until now, the appropriate methimazole dose has relied on the delicate experience and judgment of doctors. The study quantified valuable experiences gained in the clinic, giving a glimpse into the possibility of an artificial intelligence model that helps medical staff make decisions accurately and quickly. In the future, we will strive to advance the model and establish an optimal customized treatment strategy for each patient's characteristics."
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.