Korean stroke awareness improved, but in-depth understanding decreased
May 16, 2025
|
According to the study, the level of stroke awareness in Korean society improved overall, but the in-depth understanding of various risk factors decreased. In addition, the rate of information acquisition through digital platforms has increased rapidly, and the rate of intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) recognition and emergency response has increased, but it is still inadequate. This result suggests that although the overall level of stroke awareness has improved, the depth of information is insufficient and the digital information gap remains a problem.
Stroke is a disease that causes acute brain damage to the brain due to clogged or ruptured blood vessels in the brain, and is one of the main causes of death.
The incidence rate continues to increase with the increase of the elderly population, and as of 2021, the incidence of stroke in Korea is 212.2 cases per 100,000 people and more than 1,500 cases in the elderly aged 80 or older.
Major symptoms include paralysis of one arm or leg, speech impairment, facial distortion, and decreased consciousness. If a stroke is suspected, report it to 119 immediately and require quick treatment. Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, heart disease (heart disease), and a family history of stroke, and managing these risk factors is important for prevention.
However, in Korea, if the symptoms are mild, they do not receive timely first aid, causing delays in arrival to the hospital, and the implementation rate of acute treatment is still low. Hi, Shortening the delay in hospital arrival is essential for active acute stroke treatment such as intravenous thrombolysis.
Previous studies have reported that hospital arrival delays are prolonged, and these delays are more pronounced, especially when stroke symptoms are mild. This can delay acute treatment and eventually worsen the prognosis of stroke.
To solve this problem, the research team tried to analyze changes in perception of stroke and information acquisition path changes and prepare basic data for establishing effective educational strategies in the future.
This study is a nationwide survey comparing stroke perception levels at two time points in 2009 and 2023, with a telephone survey of 1000 people in 2009 and an online web survey of 1012 people in 2023. Both surveys were conducted in a stratified sample method that secured national representation through proportional allocation sampling based on demographics and considered gender, age, and region. The survey evaluated the perception of appropriate response in the event of ▲ stroke warning symptoms ▲ risk factors ▲ treatment ▲ symptoms.
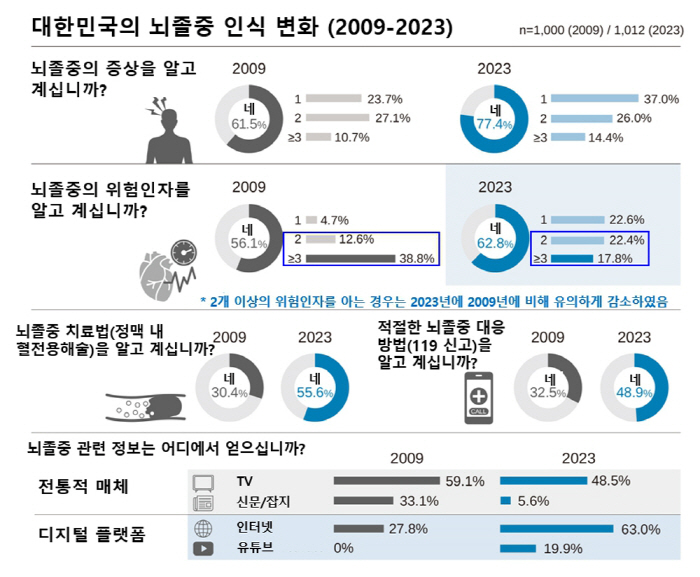
As a result of the study, awareness of stroke warning symptoms increased to 77.4% in 2023, compared to 2009 (61.5%), but recognition of two or more risk factors decreased from 51.4% to 40.2%. In particular, decreased awareness was noted in the group without vascular risk factors, suggesting that information vulnerable class still exists.
In addition, in 2023, awareness of intravenous thrombolysis increased significantly from 30.4% to 55.6%, and the rate of choosing 119 when stroke symptoms occurred also increased from 32.5% to 48.9%. The analysis showed that recognition of intravenous thrombolysis (adjusted odds ratio =1.54) and recognition of two or more warning symptoms (adjusted odds ratio =1.43) were significantly associated with increased probability of 119 reporting. In other words, people with intravenous thrombolysis recognition and two or more warning symptoms are more likely to report to 119 when stroke symptoms occur.
On the other hand, in groups under the age of 40 and with unhealthy lifestyles (smoking, binge drinking, lack of exercise, etc.), the probability of responding appropriately to stroke symptoms was low. This means that these groups lack awareness of stroke or emergency response behavior.
The path of obtaining health information has changed significantly over the past 14 years. While the rate of information acquisition through TV decreased from 59.1% in 2009 to 48.5% in 2023, the rate of information acquisition through digital media such as the Internet (27.8% → 63.0%) and YouTube (0% → 19.9%) increased significantly.
Professor Geun-Hwa Chung (neurology) said, "This is the first large-scale study to assess changes in stroke perception at two time points in 2009 and 2023, with improved overall perception but decreased depth of information."Especially among young people and those without existing vascular risk factors, the tendency to perceive it as 'something unrelated to me' may be a major cause of missing opportunities for early response.", he explained.
In the future, it is urgent to develop differentiated educational strategies tailored to age, health behavior, and the presence or absence of underlying diseases and reliable digital-based educational content. "We plan to expand our research toward developing customized educational strategies for each age group and evaluating the practical effects of awareness improvement linked to actual behavioral changes."
Meanwhile, the study was conducted with the support of the National Institute of Health of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Korean Stroke Association, and the Central Cardiovascular Disease Center, and the results were published in the latest issue of the American Heart Association.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.