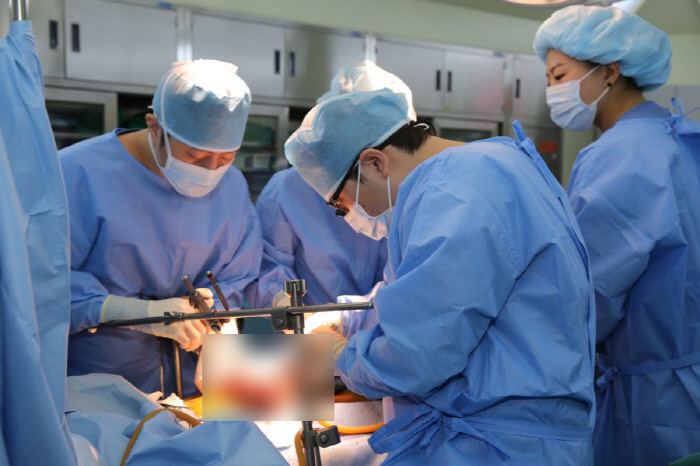
Liver and kidney living organs transplant, is there no problem with donors?
May 14, 2025
|
N2MT07||text parameter is needed (text 파라미터가 필요합니다.)
Liver transplantation is the best treatment method for cirrhosis, liver cancer, and end-stage liver disease, but due to misunderstanding, it has not been activated due to opposition from patients and families and negative perceptions that conditions are difficult and side effects and risks are high between transplant recipients and donors.
◇Even if you cut part of the liver, it will be played in about 3-6 months...Only 1% of cases require donor treatment
The liver has excellent regenerative ability, so even if a part of a living human liver is cut off, both donors and recipients can restore liver function after a certain period of time. Basically, we need a donor who can donate a healthy liver, but in the past, liver transplantation was performed only when the donor and recipient had the same blood type or blood transfusion was possible, and physical conditions such as height and weight were similar.
Recently, with the development of immunosuppressants and treatments, liver transplantation is possible even if the blood type between the donor and the patient is inconsistent, and the success rate and survival rate are also very high, more than 95%.
Seo Seok-won, director of the Organ Transplantation Center at Chung-Ang University Hospital, said, "In the West, organ donations from brain-dead people are active, and in Korea, organ donations from brain-dead people are very scarce, so as an alternative to this, 'living liver transplantation' is currently being performed by transplanting part of the liver of a normally active person, but this is also often missed due to misunderstanding and negative perception."
While living liver transplantation is carried out in Korea at about 20 people per 1 million people a year, a recent study by a university hospital in Korea found that the survival rate of patients who received living liver transplantation was nearly three times higher than that of patients waiting for brain-dead liver transplantation, and the risk of death after liver transplantation was low.
Professor Seo Seok-won said, `Currently, living liver transplants account for more than two-thirds of all liver transplants, and the success rate of living liver transplants in 10 hospitals in Korea has been high at 97.6%. Based on the medical staff's extensive experience, management before and after surgery has been standardized, development of surgical techniques, immunosuppressants, and improvement of infection control levels have achieved excellent treatment results."
Even if the actual blood type is different, recently, blood type nonconforming liver transplantation has been successfully performed by administering a drug to suppress the production of blood type antibodies in bone marrow three weeks before liver transplantation and performing plasma exchange to remove existing blood type antibodies a week before surgery.
In addition, liver donation is performed when various health conditions are good and liver function and liver size are normal, and most of them are used to resect and transplant parts of the right liver, which accounts for 65-70% of the total liver, and even if a part of the liver is cut off, it regenerates itself after about 3-6 months and almost recovers to its original state.
Professor Seo Seok-won said, `There is usually no problem with the donor in liver transplantation, and most of the cases improve on their own without special treatment after surgery.' `It is known that only about 1% of donors need therapeutic procedures, and there are no reports of disability or death after liver donation surgery in Korea, so if you have received a sufficient preliminary examination and found that it is suitable for donation, you can transplant with confidence.'
◇Survival rate of end-stage renal failure patients with kidney transplants 80-90%…It's possible even if your blood type is different
One of the organs that can be transplanted to others while alive as well as liver transplantation is the kidney.
Kidney transplantation is performed in a state of end-stage renal failure in which the function of the kidney is almost gone. In end-stage renal failure, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is generally performed to replace the kidney's function, and not only does dialysis limit daily life due to the time required for dialysis, but because dialysis cannot replace 100% of the normal kidney function, the five-year survival rate of patients with end-stage renal failure is about 75%, similar to the five-year survival rate of cancer patients in Korea.
On the other hand, the survival rate of end-stage renal failure patients who received kidney transplantation is high at about 80-90%, and the quality of life is greatly improved by not having to undergo regular dialysis treatment.
However, since there are more people waiting for brain death kidney transplants than domestic brain death donors, the average waiting period for brain death is 8 to 10 years, so if there is a donor who will donate because many patients die waiting for brain death kidney transplants or get tired waiting for brain death transplants, a living transplant is recommended.
Since a healthy person has two kidneys, even if one kidney is donated, a healthy person can continue a healthy life with the remaining one, so living kidney transplants are more active than liver transplants, and 60.7% of Korean kidney transplants are living transplants.
Professor Soi Kwon of the Department of Nephrology at Chung-Ang University Hospital said, `The survival rate of end-stage renal failure patients who received kidney transplants is about 80-90%, and the quality of life and survival rate are greatly improved by not having to undergo regular dialysis treatment"We actively recommend kidney transplants to end-stage renal failure patients because kidney transplantation is not only an ideal treatment but also a hope for end-stage renal failure patients who are in despair that the immune system does not attack the transplanted kidney."
If there is a donor, the donor will conduct an overall medical examination on whether they can stay healthy even after donating, and check the donor's renal function through various tests before proceeding with the transplant.
Living kidney transplantation is a surgical process in which the donor's kidney is extracted and the kidney is transplanted to the recipient, and the donor can be discharged from the hospital if there are no complications three days after the operation.
Recently, transplants are possible even if donors and recipients do not have the same blood type, and immunosuppressive treatment is performed to remove the recipient's antibodies to reduce the likelihood of rejection after transplantation.
Professor Soi Kwon said, "As treatment through kidney transplantation develops, more secure donation can save lives through fundamental treatment of many patients."If we overcome the fear of transplantation and all patients and their families perform transplantation with an active will, we can no longer go on dialysis and enjoy a healthy life. "
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.