Hyundai Engineering & Construction to reduce global greenhouse gases with floating CCS technology
Aug 14, 2025
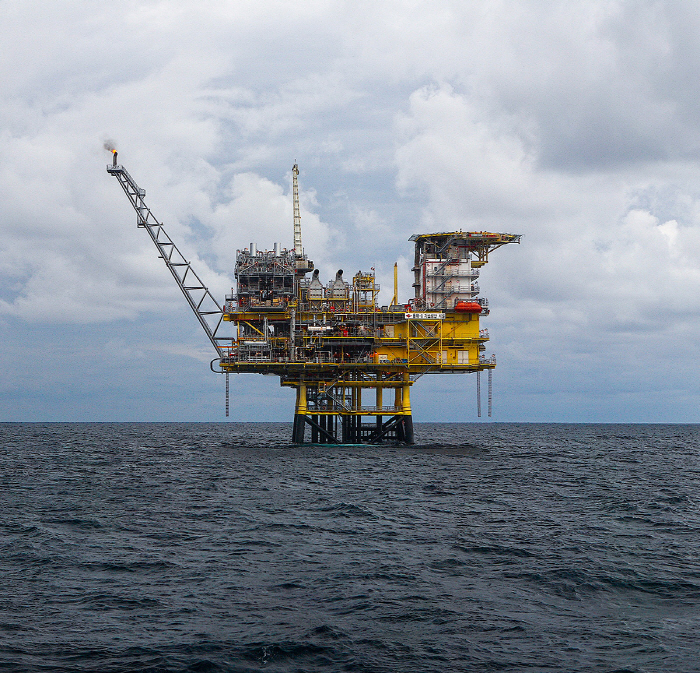
Hyundai Engineering & Construction will help reduce greenhouse gases using offshore oil and gas fields in Southeast Asia with floating body-based CCS technology.
N2MT07||text parameter is needed (text 파라미터가 필요합니다.)
Hyundai Engineering & Construction signed an agreement with the Korea Energy Technology Evaluation Institute under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy on the 13th on 'Development of Subsequent Transfer Expandable Floating CCS Facilities and CO₂ Injection Concept/Basic Design Technology for Distributed CCS Storage in Southeast Asia' and will conduct international joint research with eight private, government and academic institutions for a total of 42 months. CCS technology is a technology that collects emitted carbon dioxide and safely injects it deep in the ground and stores it permanently.
Hyundai Engineering & Construction's national project this time is to secure the concept and basic design (FEED) technology of a floating CO₂ injection system to use depleted oil and gas fields in Southeast Asia's maritime regions as carbon dioxide storage, with a total research cost of 5.8 billion won. Hyundai Engineering & Construction, the lead research institute, is in charge of the study, and eight institutions, including the Korea National Oil Corporation, the American Shipment Association, Seoul National University, and Indonesia's Pertamina University, will participate in the study.
Until now, marine carbon dioxide storage has been injecting CO₂ through structures and pipes fixed under the sea. However, if the storage is scattered in several places, such as in Southeast Asia, the floating type that can be used by moving the modular injection facility sequentially is much more efficient.
In this study, Hyundai Engineering & Construction plans to develop a CO₂ injection system using floating concrete that can float on the sea in addition to floating objects using ships, and to derive a business model by securing a basic design approval (AIP). In particular, as infrastructure construction costs are planned to be reduced by 25% compared to the existing fixed method, it is expected to play a role in expanding the CCS business in Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, in the future.
In addition, this floating CCS technology is highly utilized in blue hydrogen and blue ammonia businesses. This is because if an infrastructure is established that can directly process carbon dioxide generated during hydrogen or ammonia production in the ocean, carbon emissions during the entire production, storage, and transfer process can be minimized. Through this study, Hyundai Engineering & Construction is considering expanding to offshore carbon neutral clusters such as floating hydrogen production and offshore ammonia synthesis facilities.
Meanwhile, Hyundai E&C will collaborate with Malaysia and the Netherlands to conduct CCUS research using depleted oil and gas fields from 2022 and participate in the preliminary basic design of CCS demonstration projects utilizing Donghae gas fields, the first CCS commercialization project in Korea, from 2023 to expand its influence to leading companies in related fields. Also, 'CO₂ capture for blue hydrogen production?It is also focusing on securing CCUS' entire value chain capabilities by carrying out a national project called 'Liquidation? Utilization Technology Development'.
Hyundai Engineering & Construction plans to meet the government's carbon neutrality policy by upgrading CCUS core technologies and expanding business areas through energy mixes such as nuclear power plants, hydrogen, and renewable energy, while strengthening global competitiveness in climate crisis response projects.
N2MT07||text parameter is needed (text 파라미터가 필요합니다.)
Hyundai Engineering & Construction signed an agreement with the Korea Energy Technology Evaluation Institute under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy on the 13th on 'Development of Subsequent Transfer Expandable Floating CCS Facilities and CO₂ Injection Concept/Basic Design Technology for Distributed CCS Storage in Southeast Asia' and will conduct international joint research with eight private, government and academic institutions for a total of 42 months. CCS technology is a technology that collects emitted carbon dioxide and safely injects it deep in the ground and stores it permanently.
Hyundai Engineering & Construction's national project this time is to secure the concept and basic design (FEED) technology of a floating CO₂ injection system to use depleted oil and gas fields in Southeast Asia's maritime regions as carbon dioxide storage, with a total research cost of 5.8 billion won. Hyundai Engineering & Construction, the lead research institute, is in charge of the study, and eight institutions, including the Korea National Oil Corporation, the American Shipment Association, Seoul National University, and Indonesia's Pertamina University, will participate in the study.
Until now, marine carbon dioxide storage has been injecting CO₂ through structures and pipes fixed under the sea. However, if the storage is scattered in several places, such as in Southeast Asia, the floating type that can be used by moving the modular injection facility sequentially is much more efficient.
In this study, Hyundai Engineering & Construction plans to develop a CO₂ injection system using floating concrete that can float on the sea in addition to floating objects using ships, and to derive a business model by securing a basic design approval (AIP). In particular, as infrastructure construction costs are planned to be reduced by 25% compared to the existing fixed method, it is expected to play a role in expanding the CCS business in Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, in the future.
In addition, this floating CCS technology is highly utilized in blue hydrogen and blue ammonia businesses. This is because if an infrastructure is established that can directly process carbon dioxide generated during hydrogen or ammonia production in the ocean, carbon emissions during the entire production, storage, and transfer process can be minimized. Through this study, Hyundai Engineering & Construction is considering expanding to offshore carbon neutral clusters such as floating hydrogen production and offshore ammonia synthesis facilities.
Meanwhile, Hyundai E&C will collaborate with Malaysia and the Netherlands to conduct CCUS research using depleted oil and gas fields from 2022 and participate in the preliminary basic design of CCS demonstration projects utilizing Donghae gas fields, the first CCS commercialization project in Korea, from 2023 to expand its influence to leading companies in related fields. Also, 'CO₂ capture for blue hydrogen production?It is also focusing on securing CCUS' entire value chain capabilities by carrying out a national project called 'Liquidation? Utilization Technology Development'.
Hyundai Engineering & Construction plans to meet the government's carbon neutrality policy by upgrading CCUS core technologies and expanding business areas through energy mixes such as nuclear power plants, hydrogen, and renewable energy, while strengthening global competitiveness in climate crisis response projects.
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.