Young Dementia Surges 3.7 Times in 10 Years...Misunderstood as stress, depression, menopausal symptoms, late diagnosis
Sep 03, 2025
|
Although the proportion of patients with 'premature dementia' that develop before the age of 65 is still low, the problem is that the increase is unusual.
According to a survey by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institute of Health, the number of premature dementia patients surged 3.7 times from about 17,000 in 2009 to about 63,000 in 2019.
Increasing factors can be attributed to increased early diagnosis, improved awareness of dementia diseases, lifestyle, and social factors.
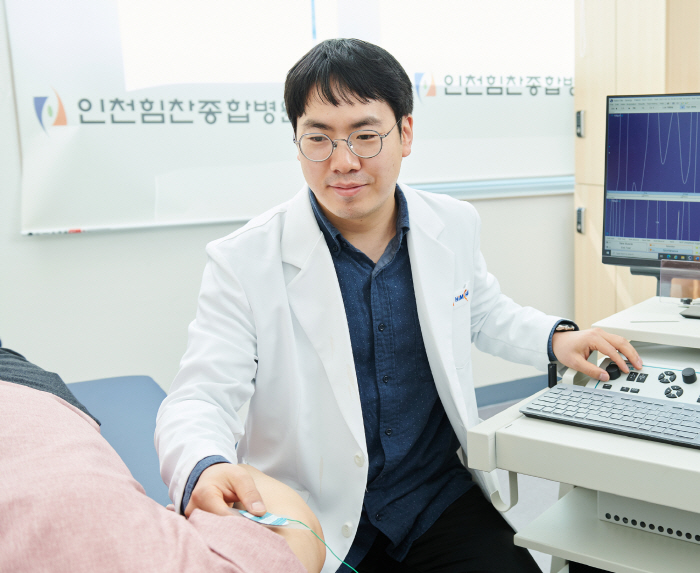
Park Jung-hoon, director of the Department of Neurology at Himchan General Hospital in Incheon, explained, `It seems to be closely related to the increased risk of cerebrovascular and metabolic diseases caused by diabetes, high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, obesity, smoking, drinking, and lack of sleep.'
The diagnosis of 'young dementia' is often delayed. This is because it is mistaken for work stress, depression, and menopausal symptoms.
◇'Young dementia', worse than the elderly...'Film' If it breaks off, the risk of dementia is two to three times higher within 10 years
The main causes of premature dementia are Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, frontal temporal lobe dementia, and alcoholic dementia.
Alzheimer's dementia accounts for about a third of all premature dementia causes and often has a family history.
Memory loss is noticeable, and unlike common dementia, symptoms such as headaches, muscle cramps, and walking disorders are often accompanied.
In general, vascular dementia, which occurs around the age of 30, is often caused by cerebrovascular damage. It is associated with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes, and mainly suffers from migraines and cognitive decline.
Front temporal lobe dementia, which occurs frequently in the 40s and 60s on average, is caused by regression of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, and personality changes, impulse control disorders, and speech disorders occur.
If brain cells are damaged due to excessive drinking for a long time, the possibility of alcoholic dementia increases. Major symptoms include personality changes such as decreased memory and judgment, increased aggression, and depression. Some studies show that if you have experienced at least one so-called 'blackout' that your memory is lost after drinking alcohol, the risk of dementia within 10 years is two to three times higher.
Premature dementia is more severe than dementia in the elderly.
This is because complex problems such as job retention, child rearing, and social relations are intertwined.
Park Jung-hoon, director of the center, said "If it occurs in the age group that is active at work and at home, job loss can put a burden on family support and cause long-term family care stress." In addition, some premature dementia (especially Alzheimer's disease, frontal temporal dementia) often progress faster than the elderly.
|
Early diagnosis and identification of the exact cause of premature dementia are important.
This is because damaged brain cells cannot be revived and there are many genetic factors, making it difficult to cure them at present.
The key to treatment is to slow the progression of the disease and maintain the quality of life by improving life such as drugs, exercise, cognitive rehabilitation treatment, smoking cessation and abstaining.
The same goes for prevention.
To this end, the National Medical Center's Central Dementia Center recommends the 「3·3·3 Rules for Dementia Prevention」.
He emphasized the need to enjoy 'exercise, meals, reading', avoid alcohol, cigarettes, brain damage', and take care of 'health check-ups, communication, and early detection'.
It is recommended to practice aerobic exercises such as fast walking, cycling, swimming, hiking, and dancing at least 30 minutes a day and five times a week.
It is recommended to maintain the intensity of the exercise that increases the heart rate and makes you sweat slightly.
It is helpful to do muscle exercises such as squats, planks, and raising dumbbells two to three times a week.
Yoga, Pilates, and stretching are good for relieving stress and improving sleep.
It is important to eat nutrient-rich foods evenly in the diet.
On a daily basis, it is good to consume 100g of whole grains (brown rice, oats, whole wheat bread, etc.), a handful of nuts (almond, walnut, etc.) (about 30g), 100g of legumes and vegetable proteins (tofu, lentils, etc.), 150g of vegetables, half a strawberry paper cup, and one tablespoon of olive oil every day. It is recommended to eat white meat (chicken, duck meat, etc.) and fish (salmon, mackerel, etc.) at least twice a week.
Processed meat, trans fats, refined carbohydrates, sweet drinks, snacks, fried foods, margarine, etc. should be avoided.
Experts advised that `the most important thing for the prevention of dementia is vascular health and maintenance of an antioxidant diet' and"it is important to eat various nutrients in a balanced way, not to limit them too extreme or rely solely on specific foods.'
Park Jung-hoon, head of the center, added "It is better to increase brain stimulation activities and maintain social exchanges by continuing new learning such as reading, musical instruments, and learning foreign languages."
|
This article was translated by Naver AI translator.